
To interpret the result, values between 0.5 and 1 (for example our value of 0.88) indicate that the value we are calculating the probability for is somewhere between the mean and the right tail of the distribution. The result will tell us the probability of the random variable from a normal distribution being less or equal to a specific value. The NORM.DIST function gives us us the probability of a certain value occurring in a normal distribution. The syntax for the NORM.DIST function is as follows:Īnd one more for probability density (using FALSE) in column E: Interpreting the Results of Normal Distribution Probability This function takes into account the value for which we are finding the probability, the mean, and the standard deviation, and checks if we want the cumulative distribution or the probability density. To calculate the probability of a certain value lined above occurring in a normal distribution, we will use NORM.DIST function. Calculate Normal Distribution Probability in Excelįor our example, we will use three values that will be located in column A:
Calculating normal distribution percentages in excel how to#
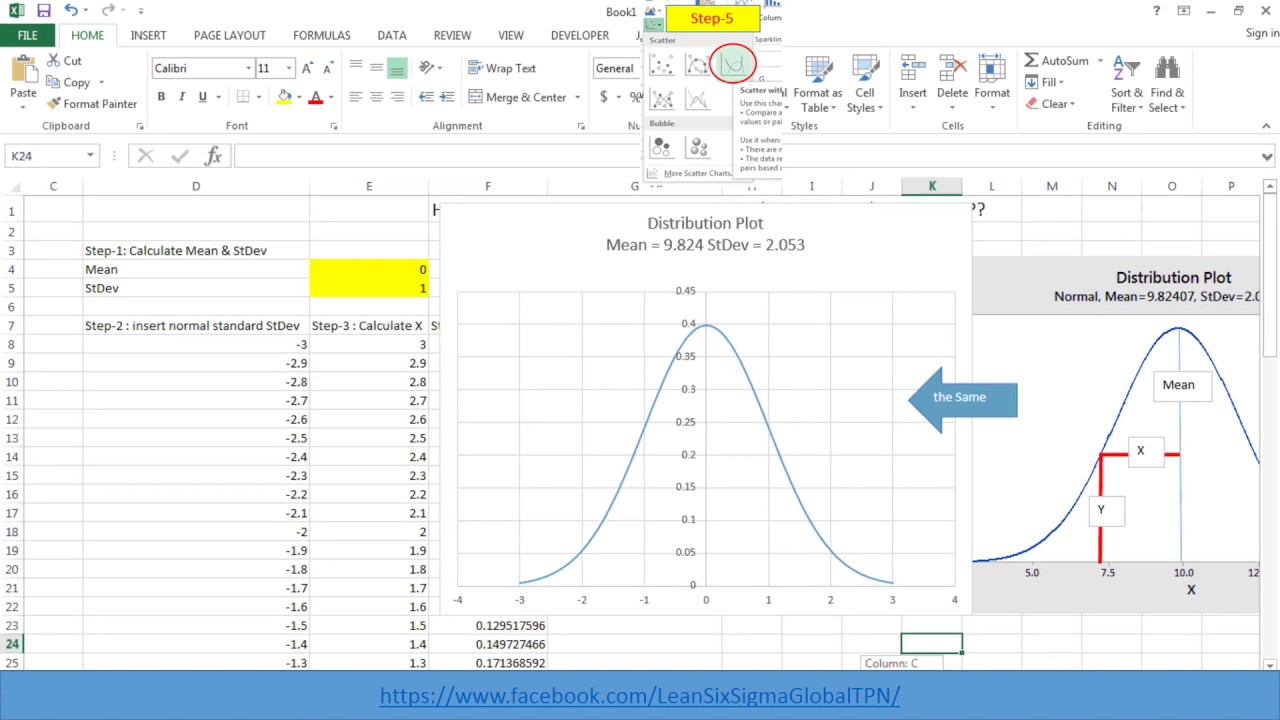
In the example below, we will show how to calculate the probability of a value occurring in a normal distribution. What it shows is that the data near the mean occur more often than data far from the mean.
It is also known as Gaussian distribution, and it gives us the probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean. One of these terms is normal distribution. There are a lot of statistical measures and terms that are used and can be calculated using Excel.
Calculate-Normal-Distribution-Probability-in-Excel Download File


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
